Journal Information
Journal ID (publisher-id): BM
Journal ID (nlm-ta): Biochem Med (Zagreb)
Title: Biochemia Medica
Abbreviated Title: Biochem. Med. (Zagreb)
ISSN (print): 1330-0962
ISSN (electronic): 1846-7482
Publisher: Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Article Information
Copyright statement: ©Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
Copyright: 2025, Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry
License (open-access):
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Date received: 05 December 2024
Date accepted: 10 March 2025
Publication date: 15 June 2025
Publication date: 15 June 2025
Volume: 35
Issue: 2
Electronic Location Identifier: 020802
Publisher ID: bm-35-2-020802
DOI: 10.11613/BM.2025.020802
Routine data analysis for moderate hemolysis interference correction in neuron specific enolase quantification
Leyre Ruiz[1]
Tomás Munoz[2]
Author notes:
The last two authors contributed equally.
[*] Corresponding author: ealegre@unav.es
Author contributions
L Ruiz and T Munoz: Investigation; A González and E Alegre: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing
• A moderate hemolysis correction formula has been developed for neuron specific enolase (NSE) quantification
• Formula is based on real routine hemolyzed samples, and not in spiked-in samples
• Calculated NSE presents a minimal bias compared to non-interfered NSE
• Correction formula avoids NSE cancelations due to moderate hemolysis in the samples
• This avoids results delays and multiple blood extractions
Introduction
Serum neuron specific enolase (NSE) is used as neuroendocrine tumor and central nervous system damage marker. It is present in variable concentrations in erythrocytes and hemolysis interferes in serum NSE quantification. Our aim was to develop a correction formula for moderate hemolysis, based on repeated patient samples instead of artificial sample doping with hemolysates.
Materials and methods
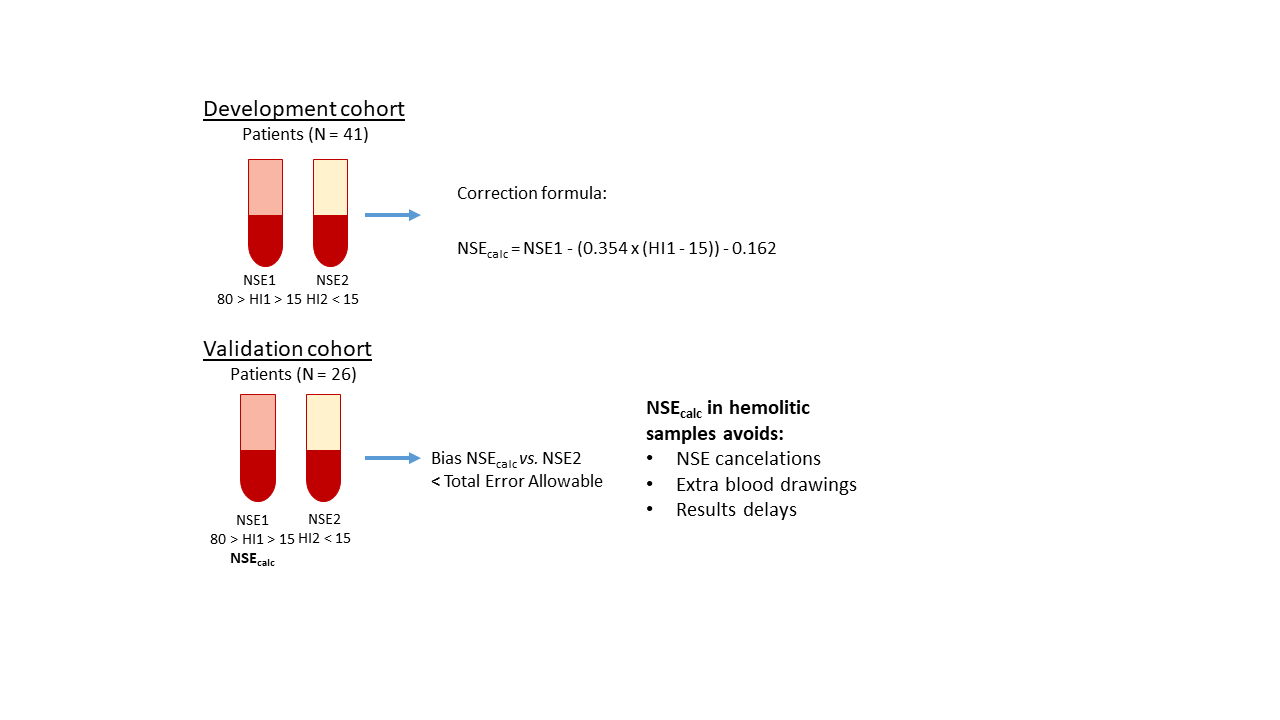
We searched in laboratory informatics system for patients with sample pairs obtained within 24 h, for NSE quantification. We registered NSE and hemolytic index (NSE1 and HI1) from the first moderate hemolyzed sample (HI: 15-80), and from the second non-hemolyzed sample obtained afterwards (NSE2 and HI2). In a development cohort (N = 41), we obtained the formula NSEcalc = NSE1 - (0.354 x (HI1 - HI2)) - 0.162, which was later used in the validation cohort (N = 26) to calculate NSE corrected concentrations (NSEcalc).
Results
Concentrations of NSE2 differed from NSE1 (P = < 0.001) but not from NSEcalc (P = 0.291). In 84% samples, NSE1 had a relative bias from NSE that exceeded the 14% limit of total error allowable, with a median relative bias of 22.5%. Meanwhile, the bias between NSE2 concentrations and NSEcalc was - 0.4 µg/L (95% confidence interval = - 3.8 to 4.5), the relative bias was 8.3% and only 23% of samples exceeded the 14% limit. Formula usefulness was limited to moderate hemolytic samples.
Keywords: NSE; hemolysis; interference; correction formula